Write a program to test whether a number n, entered through the keyboard is prime or not by using different algorithms you know for at least 10 inputs. Note down the time complexity for each algorithm along with each input. Finally make a comparison of time complexities found for different inputs, plot an appropriate graph & decide which algorithm is faster.
Table:
SL No. | Input (n) | Prime Number Testing | ||
Algo- 1 Time complexity | Algo – 2 Time complexity | Algo – 3 Time complexity | ||
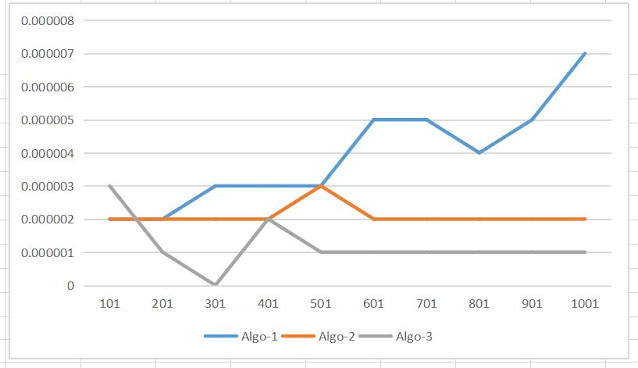
1 | 101 | 0.000002 | 0.000002 | 0.000003 |
2 | 201 | 0.000002 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 |
3 | 301 | 0.000003 | 0.000002 | 0.000000 |
4 | 401 | 0.000003 | 0.000002 | 0.000002 |
5 | 501 | 0.000003 | 0.000003 | 0.000001 |
6 | 601 | 0.000005 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 |
7 | 701 | 0.000005 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 |
8 | 801 | 0.000004 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 |
9 | 901 | 0.000005 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 |
10 | 1001 | 0.000007 | 0.000002 | 0.000001 |
Program
#include<stdio.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<math.h>
int f1(int n)
{
int c = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (n % i == 0)
c++;
}
}
int f2(int n)
{
static int i = 2;
if (n== 0||n==1) {
return 1;
}
if (n == i)
return 0;
if (n % i == 0)
return 1;
i++;
return f2(n);
}
int f3(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= sqrt(n); i++)
if (n % i == 0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
clock_t start, end;
printf("Enter 10 random values: ");
int a[10];
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
scanf(" %d", &a[i]);
}
printf("n\t\tfn1\t\t\tfn2\t\t\tf3");
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
int num = a[i];
printf("\n%d\t\t", num);
start = clock();
f1(num);
end = clock();
printf("%lf\t\t", ((double)end - (double)start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
start = clock();
f2(num);
end = clock();
printf("%lf\t\t", ((double)end - (double)start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
start = clock();
f3(num);
end = clock();
printf("%lf", ((double)end - (double)start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
}
Output
Tags:
DAA